Overview
ComponentKit really shines when used with a UICollectionView.
Automatic reuse
Who hasn't had bugs with cell reuse? In ComponentKit, the declarative nature of a Component makes it so you don't have to worry about reuse anymore! This article in objc.io explains in great detail how we achieve automatic reuse and reconfiguration with ComponentKit.
Scroll performance
ComponentKit addresses common scroll performance issues holistically. Putting cells on screen is usually very performance sensitive. Cells are dequeued during scrolling, so any frame drop will be immediately visible.
Automatic and optimized reuse is already great for performance. But also, because generating a component and laying it out is just a succession of pure functions working with immutable data this operation can be very easily moved to the background.
As a result, the list view infrastructure provided by ComponentKit only spends a minimal amount of time in the main thread. No more stutters due to complex view hierarchies or expensive text layout!
The data sources
ComponentKit includes a standard data source stack dedicated to render components directly in a UICollectionView, and with a bit more effort, in a UITableView.
CKDataSource
CKDataSource is at the core of the list view infrastructure. Instances of this class are agnostic to the UICollectionView API. The role of a CKDataSource is to:
- Take as input changesets containing commands and models. *e.g: "Insert at index 0 in section 1 the item representing ModelA".
- Generate and layout in the background the components associated to those changes.
- Output a changeset along with handles to the generated components so that it can be used with a
UITableViewor aUICollectionView
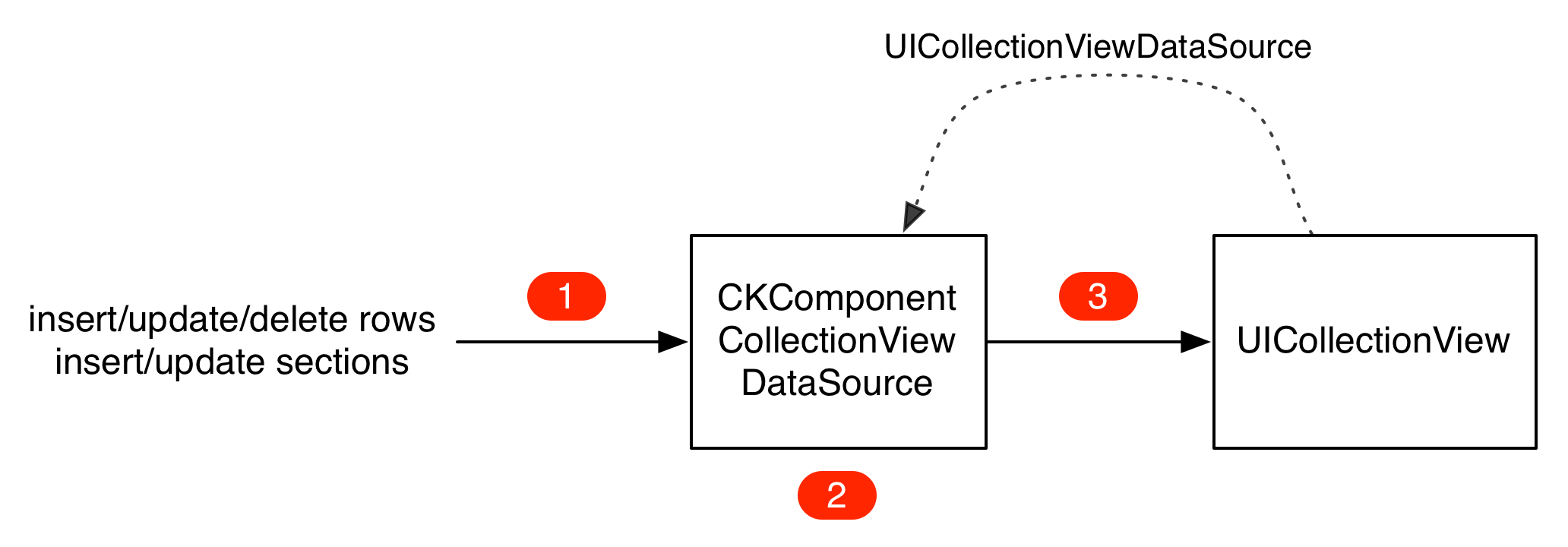
CKCollectionViewDataSource
CKCollectionViewDataSource is a thin wrapper around CKDataSource that implements the UICollectionViewDataSource API.
It can be used to easily bootstrap a UICollectionView using components. See how to display components in a collection view.
Philosophy
The UIKit way to add content to a collection view is:
- Tell the
UICollectionViewto add/insert/update rows or sections. - Synchronously, the
UICollectionViewasks its data source for number of rows, sections and layout info. - Depending on whether or not the updated index paths are visible the
UICollectionViewwill synchronously callcellForItemAtIndexPath:. - Finally, the data source returns a configured cell for this index path.
CKCollectionViewDataSource uses an idiom that is more "reactive":
- Tell the
CKCollectionViewDataSourceto add/insert/update rows or sections. - Asynchronously, and in the background, computes the corresponding components.
- When the computation is done, apply the changes to the
UICollectionView.
Conceptually, we now have a one directional data flow. Obviously the back and forth between the UICollectionView and the CKCollectionViewDataSource still happens but it is now hidden.